Citizenship of Saudi Arabia
Citizenship by birth
According to the rules of citizenship in Saudi Arabia, a person is considered a citizen if they are born to a Saudi father, both inside and outside the country. A child is also considered a citizen of the Kingdom if born to a Saudi mother and a father without citizenship, or if born in the country and their parents are unknown.
Children born in Saudi Arabia to foreign parents or to a Saudi mother and a foreign father are considered foreigners. The latter can apply for Saudi citizenship upon reaching adulthood if they meet the following conditions:
- have permanent residency;
- have exemplary behavior, no criminal convictions or imprisonment for moral crimes for more than six months;
- know the Arabic language;
- submit a request for citizenship within a year of reaching adulthood.


Citizenship through marriage
Foreign women who marry a Saudi citizen have the right to obtain citizenship of the Kingdom. To do this, several conditions must be met:
- renounce their original citizenship;
- confirm the legality of the marriage;
- the marriage must be in accordance with the rules established in the country for Saudis and foreigners;
- provide a document showing no criminal record or moral offenses;
- there should be no remarks or restrictions from the authorities regarding the applicant;
- the applicant must reside in Saudi Arabia.
Widows of Saudis can also apply for citizenship of the Kingdom. To do this, they need to:
- prove the legality of the marriage;
- renounce foreign citizenship;
- not remarry;
- reside in the territory of Saudi Arabia;
- provide a document showing no criminal record or moral offenses;
- there should be no remarks or restrictions from the authorities regarding the widow;
- have adult children from the Saudi husband.
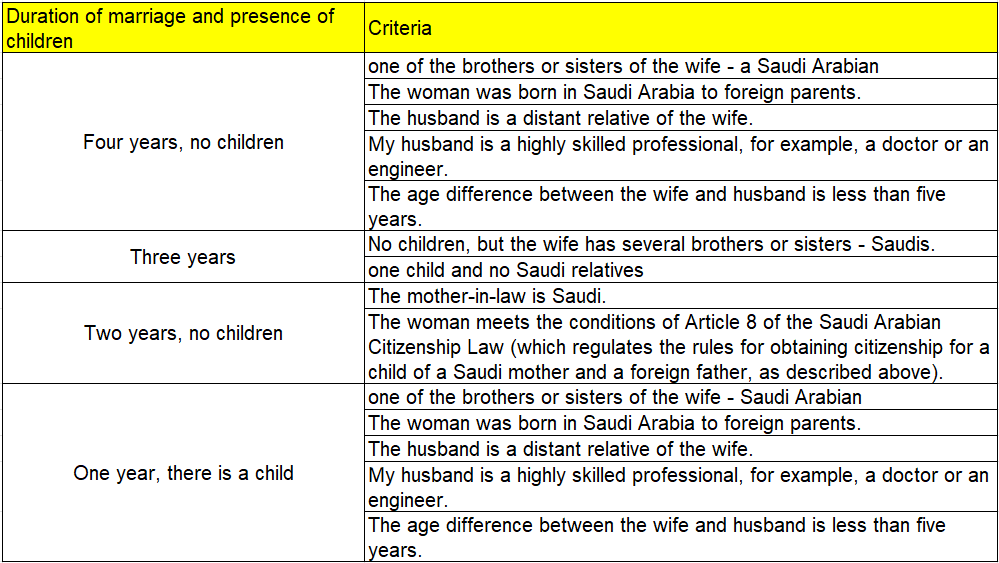
The wife of a foreigner who has obtained Saudi citizenship will also receive a passport of the Kingdom if she renounces her original citizenship within one year.

Naturalization Citizenship
In 2021, Saudi Arabia decided to grant citizenship to highly skilled foreigners. This initiative was taken as part of the Vision 2030 program, which aims to reduce the country’s dependence on oil and develop healthcare, infrastructure, education, and tourism. According to the Saudi Press Agency (SPA), citizenship is granted to world-class experts and talents with unique competencies in areas such as religion, medicine, science, culture, sports, and technology. The basic rules for obtaining citizenship through naturalization in Saudi Arabia include continuous and legal residence in the country for at least 10 years, five of which must be under permanent residency.
The legislation provides that foreigners may obtain citizenship under the following conditions:
- age over 18 years; legal capacity;
- having had a permanent residence permit for the last five years;
- good behavior, no criminal convictions;
- legality of income and stable earnings.
When a foreigner applies for Saudi Arabian citizenship, a special commission of three people is formed to confirm that the applicant:
- arrived in the country legally and has a valid passport that allows them to return to their home country;
- has resided in Saudi Arabia for at least 10 consecutive years;
- works in a profession that is in demand in the country: a scientist, doctor, engineer, or other rare professional.
The commission then evaluates the applicant based on three criteria – length of residency in Saudi Arabia, education, and family ties with Saudis – and awards them points. The maximum number of points that can be obtained is 33. If a foreigner scores more than 23 points, the commission recommends considering their application for citizenship. Foreigners working in a local company or business owners who have lived in the country for more than 10 years can apply for citizenship. However, the points system is set up in such a way that it is impossible to accumulate enough points without high qualifications or family ties in the country
